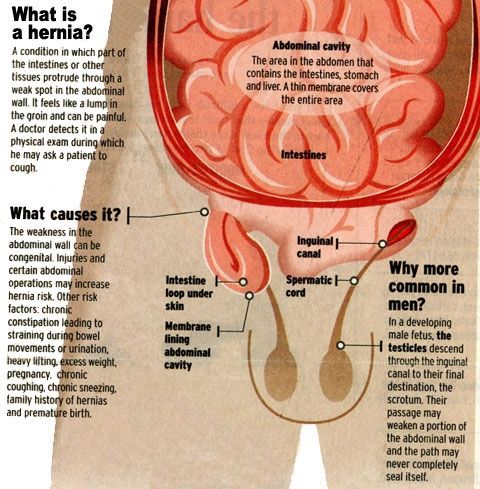
This is a medical condition that occurs when an organ or internal body part pushes its way through the tissue that is around it. A hernia can occur in numerous part of the human body like the abdomen, upper thigh, belly button, and groin areas. It is not always dangerous to human lives even though they may require surgery to prevent them mounting into new life threatening complications.
CAUSES OF HERNIA
Hernia’s are caused when there is a combination of muscle strain and mixture. It can advance into a serious a stage within a short time all depending on what started it. Muscle weakness start the moment the abdominal walls do no close appropriately in the womb and can cause chronic coughing.
If your muscles are weak, pregnancy can strain tour body to cause hernia. A heavy pressure is put on the abdomen during pregnancy, thereby constipating it. This goes on in making bowel movement painful.
SYMPTOMS
- Harsh pains in your lower region
- vomiting
- difficulty passing stools ( constipation ) or wind
- hernia becomes firm or tender, or can’t be pushed back in
When any of the above symptoms is observed, it could mean either the supply of blood to an organ trapped in the hernia has been blocked or a piece of bowel has entered and obstructed the hernia. These are real medical emergencies and should be taken very seriously.
TYPES OF HIENA
INGUINAL HERNIA
These are the most common types of hernia. They form when there’s a thin spot on your abdominal wall. An inguinal hernia can be labeled “direct” or “indirect” depending on how and when it forms. Probability is, the age and gender of the person with the hernia will have a lot to do with which type it is.
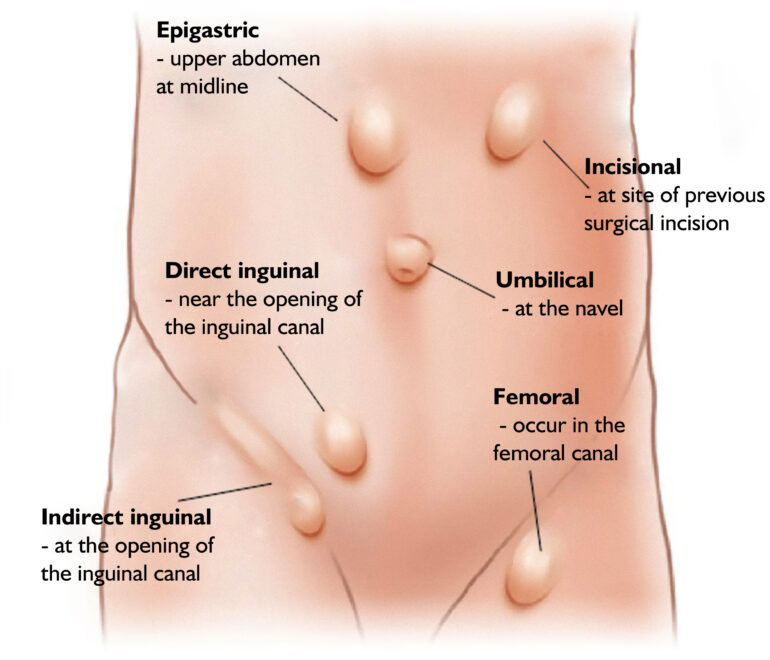
DIRECT HERNIA
A direct hernia is usually caused when the wall of the abdominal muscles becomes weak. That allows a portion of the intestine to push through the abdominal.
RISKS OF DIRECT HIENA
The Risk posed by direct hernia includes:
- smoking
- having a condition that leads to chronic coughing, such as cystic fibrosis
- having a low body mass index (BMI)
- having collagen vascular disease
It’s unclear whether heavy lifting makes it more likely that people will get hernias.
INDIRECT HERNIA
Indirect hernia’s are five times more common than the direct inguinal hernia. Due to its persistence of the processus vaginalis, it is more common in men. Indirect inguinal hernias arise lateral and superior to the course of the inferior epigastric vessels.
DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT
The doctors usually diagnose indirect hernia by physical examination alone. A bulge will appear on your groin while you are standing. The bulge is better seen when the patient is coughing. Should the hernia not be readily visible, a CT scan or MRI can be used to detect the hernia. If the hernia is not painful and not too large, you can choose to watch it without any specific therapy. Depending on your lifestyle and the discomfort level, you might choose surgery to fix the hernia. An enlarging hernia, or significant pain, will usually require surgery to alleviate the symptoms.
Any hernia that cannot be reduced will require surgery.
There are two ways for hernia treatment
- OPEN HERNIA SURGERY
- LAPAROSCOPIC SURGERY.
The open procedure requires an incision, pushing the hernia back in, and then repairing the weak area. During the laparoscopic procedure, the surgeon will repair the hernia via several small incisions and guidance by a small camera inserted through one of the incisions.
FACTORS TO CONSIDER IN DECIDING WHICH TYPE OF SURGERY IS APPROPRIATE
- The type of hernia – some types of hernia are more likely to become strangulated, or cause a bowel obstruction, than others
- The content of your hernia – if the hernia contains a part of your bowel, muscle or other tissue, there may be a risk of strangulation or obstruction
- your symptoms and the impact on your daily life – surgery may be recommended if your symptoms are severe or getting worse, or if the hernia is affecting your ability to carry out your normal activities
- your general health – surgery may be too much of a risk if your general health is poor
Types of hernia are
FEMORAL HERNIAS
Femoral hernias also occur when fatty tissue or a part of your bowel pokes through into your groin at the top of your inner thigh. They’re much less common than inguinal hernias and tend to affect more women than men. femoral hernias are also associated with ageing and repeated strain on the abdomen.
UMBILICAL HERNIAS
Umbilical hernias occur when fatty tissue or a part of your bowel pokes through your abdomen near your belly button (navel). This type of hernia can occur in babies if the opening in the abdomen through which the umbilical cord passes doesn’t seal properly after birth. Adults can also be affected, possibly as a result of repeated strain on the abdomen.
HIATUS HERNIAS
Hiatus hernias occur when part of the stomach pushes up into your chest by squeezing through an opening in the diaphragm (the thin sheet of muscle that separates the chest from the abdomen). This type of hernia may not have any noticeable symptoms, although it can cause heartburn in some people. It’s not exactly clear what causes hiatus hernias, but it may be the result of the diaphragm becoming weak with age or pressure on the abdomen.
INCISIONAL HERNIAS
Where tissue pokes through a surgical wound in your abdomen that hasn’t fully healed
EPIGASTRIC HERNIAS
Where fatty tissue pokes through your abdomen, between your navel and the lower part of your breastbone (sternum)
SPIGELIAN HERNIAS
Where part of your bowel pokes through your abdomen at the side of your abdominal muscle, below your navel
DIAPHRAGMATIC HERNIAS
Where organs in your abdomen move into your chest through an opening in the diaphragm; this can also affect babies if their diaphragm doesn’t develop properly in the womb
MUSCLE HERNIAS
Where part of a muscle pokes through your abdomen; they also occur in leg muscles as the result of a sports injury