Diabetes is a lasting disease that starts because the pancreas does not produce the sufficient insulin amount that a human body requires.
The insulin is one type of hormone which produces for the pancreas. The main function is the maintenance of an adequate level of glucose in the body. It allows glucose to enter the body and later it converted into cells. There it is transformed into the energy for tissues and muscles to function.
The high glucose level in urine and blood (read more about it here)
The two most important forms are type-1 and type-2 diabetes.
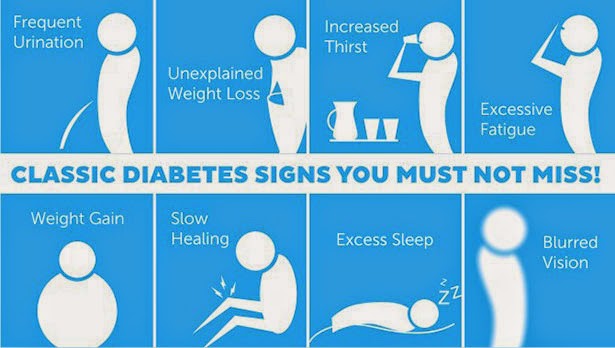
Following are the signs and symptoms of diabetes:
Diabetes often manifests itself as a strong urge to urinate and constant thirst. But also symptoms like tiredness, dry skin and frequent infections can speak for it. Here are other symptoms.
- Frequent urination
- Excessive thirst
- Weight loss
- Vomiting
- Stomach pain
- Cloudy view
- Scratches and cuts heal slowly or don’t heal
- Infections in gum, bladder, or skin
- The high glucose level in urine and blood
- Fatigue and weakness
- Unusual hunger
Treatment of diabetes:
If you are suffering from diabetes, the following are the treatment can be helpful to cure it.
- Lifestyle change:
There are many ways to treat diabetes through lifestyle changes and various medications, including insulin. It is important to select the therapy that is effective at the same time and minimizes the patient’s quality of life.
- Individual therapy goals:
The onset of changes in eyes, kidneys, and nerves can be prevented by adjusting blood glucose levels close to the norm. This should usually result in 6.5-7.5% HbA1c (blood glucose long-term memory). The choice of the HbA1c target value must always be individual. It is particularly important that this goal is achieved without heavy hypoglycemia occurring.
In individual cases, higher HbA1c levels may be an appropriate therapeutic goal. Patients with type 1 diabetes use Intensified Conventional Insulin Therapy (ICT) or Insulin Pump Therapy.
In patients with type 2 diabetes, the goal of the therapy can be achieved with lifestyle changes and tablets at the beginning of the disease. In the later stages, insulin and drugs like subcutaneously injected insulin are often required.
- Observe elevated blood pressure values:
It is known that in patients with diabetes heart attacks, strokes and circulatory disorders of the legs occur 2-3 times more often than in non-diabetics. To prevent these diseases, the lowering of blood sugar is not very effective. However, is the drug lowering of the elevated blood pressure to values below 140/85 mmHg and the treatment of elevated blood cholesterol levels with certain medications.
- Careful foot control and pedicure:
The diabetic foot is characterized by poorly healing open wounds on the feet. These wounds are caused by diabetes-related nerve damage which leads to loss of feeling and stress on the feet. In addition, there is often a circulatory disorder of the legs. The cause of the open wound of the diabetic foot is usually an injury. The wounds are often complicated by an infection. With late-onset therapy, amputations are often unavoidable.
It is very important to identify in good time those patients who are at risk of developing a diabetic foot. These patients must take proper care of their feet and should wear shoes suitable for diabetes, possibly with appropriate insoles from specialized brands such as Protalus.