Collaborative robots, or cobots, have become integral to industries by sharing tasks with humans to boost productivity, ensure safety, and optimize processes. These machines excel in repetitive and precision-oriented tasks, yet their increasing adoption highlights the need for efficient oversight.
Remote monitoring has emerged as a transformative solution, offering real-time insights and proactive management tools.
What is Remote Monitoring for Cobots?
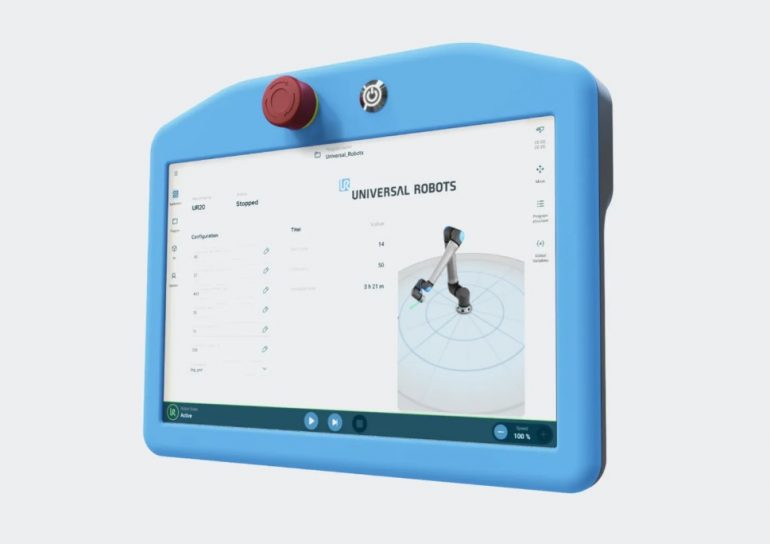
Remote monitoring refers to the ability to supervise and manage cobots from afar, often via a combination of IoT, cloud computing, and AI-driven analytics. These systems collect data from cobots, analyze it in real-time, and present actionable insights through dashboards or alerts.
The primary goal of remote monitoring is to maximize uptime and efficiency while reducing the manual effort required for on-site troubleshooting. By enabling faster response times, businesses can prevent minor issues from escalating into major disruptions.
Core Components of a Remote Monitoring System

- Sensors and data collection units ─ Sensors are the backbone of remote monitoring, capturing vital metrics such as temperature, motion, pressure, and load. Advanced sensors can even detect subtle changes in performance, allowing early intervention.
- Communication protocols ─ Technologies like MQTT, Wi-Fi, 5G, or Ethernet transmit sensor data to centralized or cloud-based servers. High-speed and low-latency communication protocols ensure that real-time insights are accurate and actionable.
- Dashboards and alerts ─ User interfaces display key performance indicators (KPIs) in intuitive formats, such as charts and graphs. Alerts, sent via email or mobile apps, notify operators of anomalies, enabling rapid responses.
- Edge computing integration ─ For environments with limited connectivity, edge computing processes data locally on cobots or nearby devices, ensuring that critical functions continue uninterrupted.
Benefits of Remote Monitoring
With continuous data collection, businesses can track and optimize cobot performance in real-time. This ensures that tasks are completed efficiently, and maintenance schedules are informed by actual wear and tear rather than arbitrary timelines.
For example, a packaging cobot operating on a production line can adjust its speed based on demand fluctuations, reducing energy consumption and avoiding unnecessary strain.
Improved Error Detection and Recovery
Error recovery is often the most time-sensitive challenge for cobot operators. Remote monitoring systems allow technicians to:
- Diagnose issues quickly ─ Identify root causes through real-time data visualization.
- Implement fixes remotely ─ Update software configurations or reset operations without physical intervention.
- Prevent future errors ─ Log and analyze error patterns to avoid recurrence.
For instance, if a cobot arm in an assembly plant shows signs of misalignment, the system can detect this deviation early and trigger a correction before it disrupts production.
Scalability and Flexibility
For companies managing multiple cobots across different facilities, remote monitoring offers a centralized way to manage operations. This scalability is especially critical for global supply chains, where downtime in one location could have a ripple effect across the network.
Remote monitoring also facilitates flexible deployment by allowing companies to experiment with cobot configurations without extensive on-site testing.
Industry Applications
Manufacturing plants rely on cobots for welding, painting, assembly, and more. Remote monitoring ensures that these tasks are carried out consistently, and deviations are addressed immediately. Predictive maintenance tools can flag wear on parts, reducing the likelihood of production halts.
In hospitals, cobots assist in patient care, from administering medication to aiding in surgeries. Remote monitoring provides an extra layer of safety by ensuring that these machines operate within strict parameters. Alerts can notify medical teams of any performance irregularities, safeguarding patient well-being.
Cobots used in warehousing tasks, such as inventory sorting and order fulfillment, benefit significantly from remote monitoring. Operators can optimize their routes, detect mechanical issues, and even predict when battery levels will require recharging, minimizing delays.
Overcoming Challenges
The increasing reliance on data-sharing technologies brings cybersecurity risks. Unauthorized access to remote monitoring systems could compromise sensitive information or disrupt operations. To mitigate these risks:
- Implement end-to-end encryption for all communications.
- Use multi-factor authentication to secure system access.
- Conduct regular security audits and updates.
Industrial environments often face connectivity challenges, whether due to remote locations or signal interference. Edge computing and hybrid systems (cloud and local servers) address these issues by ensuring uninterrupted functionality even in offline scenarios.
Many organizations face hurdles in integrating older equipment with modern monitoring platforms. Solutions such as retrofitting cobots with advanced sensors or using middleware software ensure compatibility while keeping costs manageable.
AI and Machine Learning in Remote Monitoring

AI and machine learning (ML) technologies play a crucial role in transforming how cobots are monitored and managed.
AI analyzes historical and real-time data to forecast when components may fail, enabling preemptive repairs. This predictive capability significantly extends the lifespan of cobots and reduces costly interruptions.
Machine learning models can learn from previous errors to suggest solutions or even autonomously resolve issues. For instance, an ML-powered system might detect abnormal vibrations and automatically adjust the cobot’s movement parameters to stabilize performance.
AI algorithms continuously evaluate cobot efficiency, offering recommendations to improve workflows. Over time, cobots adapt to their environments, delivering consistent gains in productivity.
Conclusion
Remote monitoring is not just a tool for enhancing cobot management—it’s a strategy for transforming how businesses approach automation. By improving efficiency, streamlining error recovery, and integrating cutting-edge technologies, remote monitoring unlocks the full potential of collaborative robots.
For companies seeking innovative solutions to optimize their cobot fleets, exploring advanced systems like those offered by Olis Robotics can provide a competitive edge. Investing in remote monitoring is an investment in the future of smarter, more sustainable automation.

